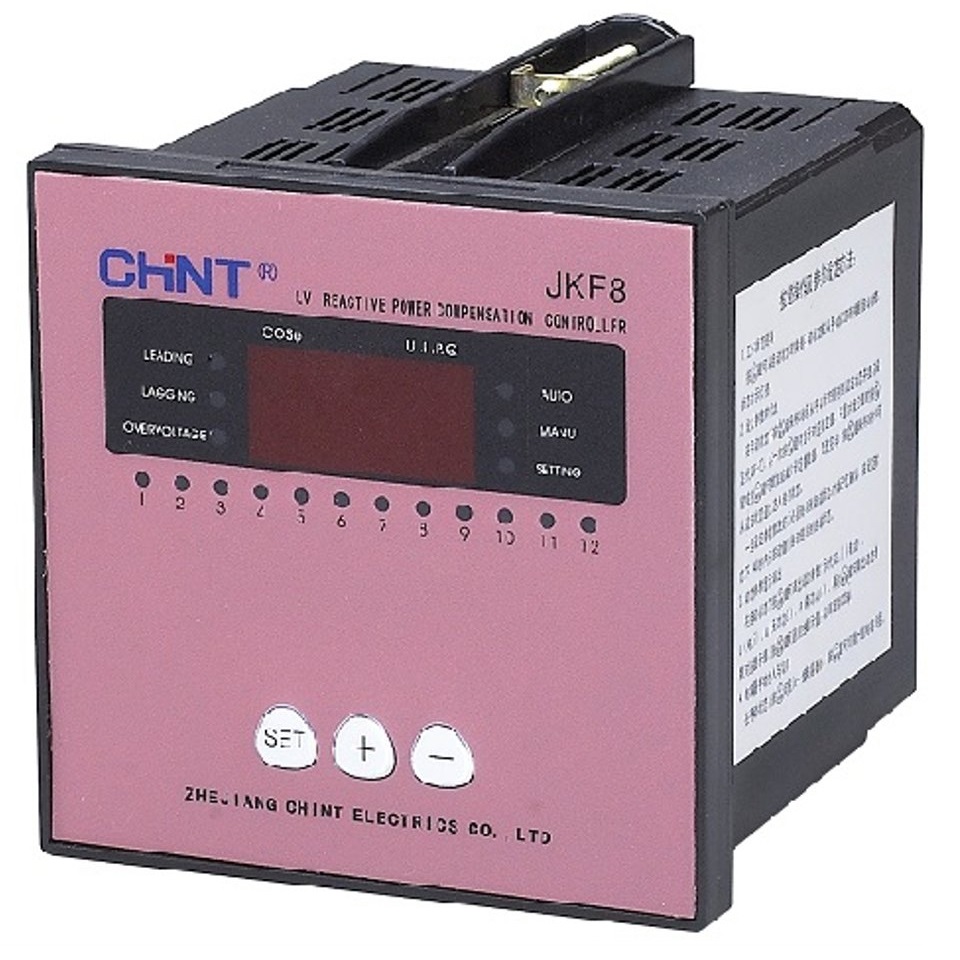
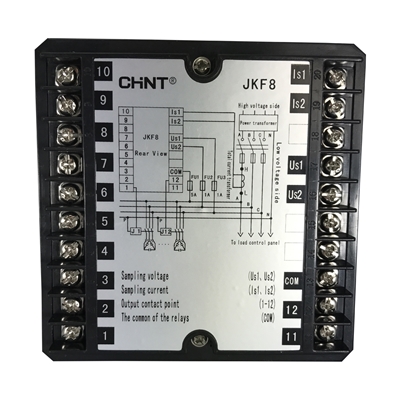
Description
- PFC (power factor correction; also known as power factor controller) is a feature included in some computer and other power supply boxes that reduces the amount of reactive power generated by a computer.
- Reactive power operates at right angles to true power and energizes the magnetic field.
- Reactive power has no real value for an electronic device, but electric companies charge for both true and reactive power resulting in unnecessary charges.
- In power factor controllers, the power factor (represented as k) is the ratio of true power (kwatts) divided by reactive power (kvar).
- The power factor value is between 0.0 and 1.00.
- If the power factor is above 0.8, the device is using power efficiently.
- A standard power supply has a power factor of 0.70-0.75, and a power supply with PFC has a power factor of 0.95-0.99.
- PFC is not used solely for computer power supplies.
- In other industries, PFC equipment is used to reduce the reactive power produced by fluorescent and high bay lighting, arc furnaces, induction welders, and equipment that uses electrical motors.
- In an electric power system, a load with a low power factor draws more current than a load with a high power factor for the same amount of useful power transferred.
- The higher currents increase the energy lost in the distribution system, and require larger wires and other equipment.
- Because of the costs of larger equipment and wasted energy, electrical utilities will usually charge a higher cost to industrial or commercial customers where there is a low power factor.
- Power-factor correction increases the power factor of a load, improving efficiency for the distribution system to which it is attached.
- Linear loads with low power factor (such as induction motors) can be corrected with a passive network of capacitors or inductors.
- Non-linear loads, such as rectifiers, distort the current drawn from the system.
- In such cases, active or passive power factor correction may be used to counteract the distortion and raise the power factor.
- The devices for correction of the power factor may be at a central substation, spread out over a distribution system, or built into power-consuming equipment.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.